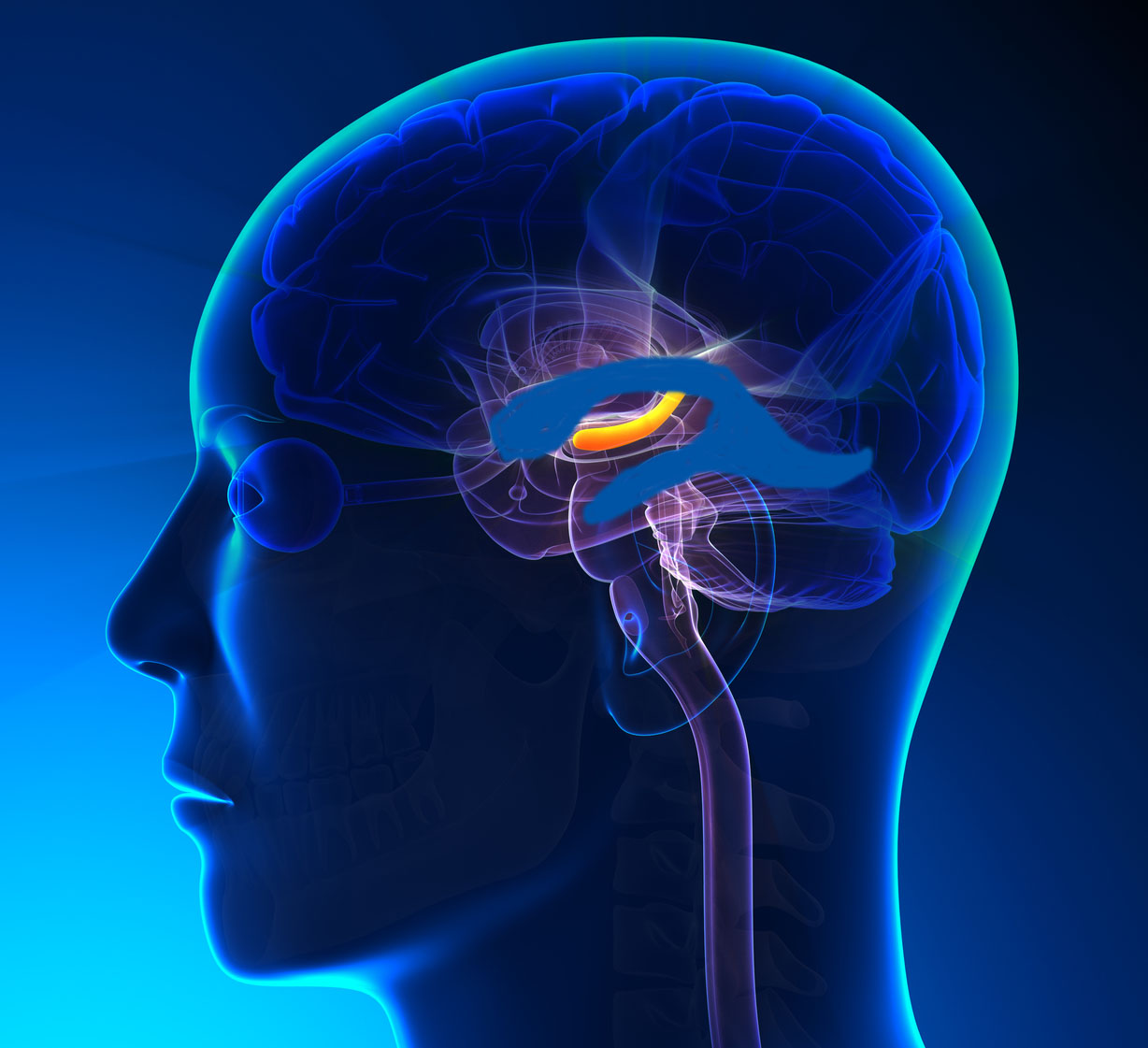
The hippocampus is orange-
yellow;the ventricles are blue.
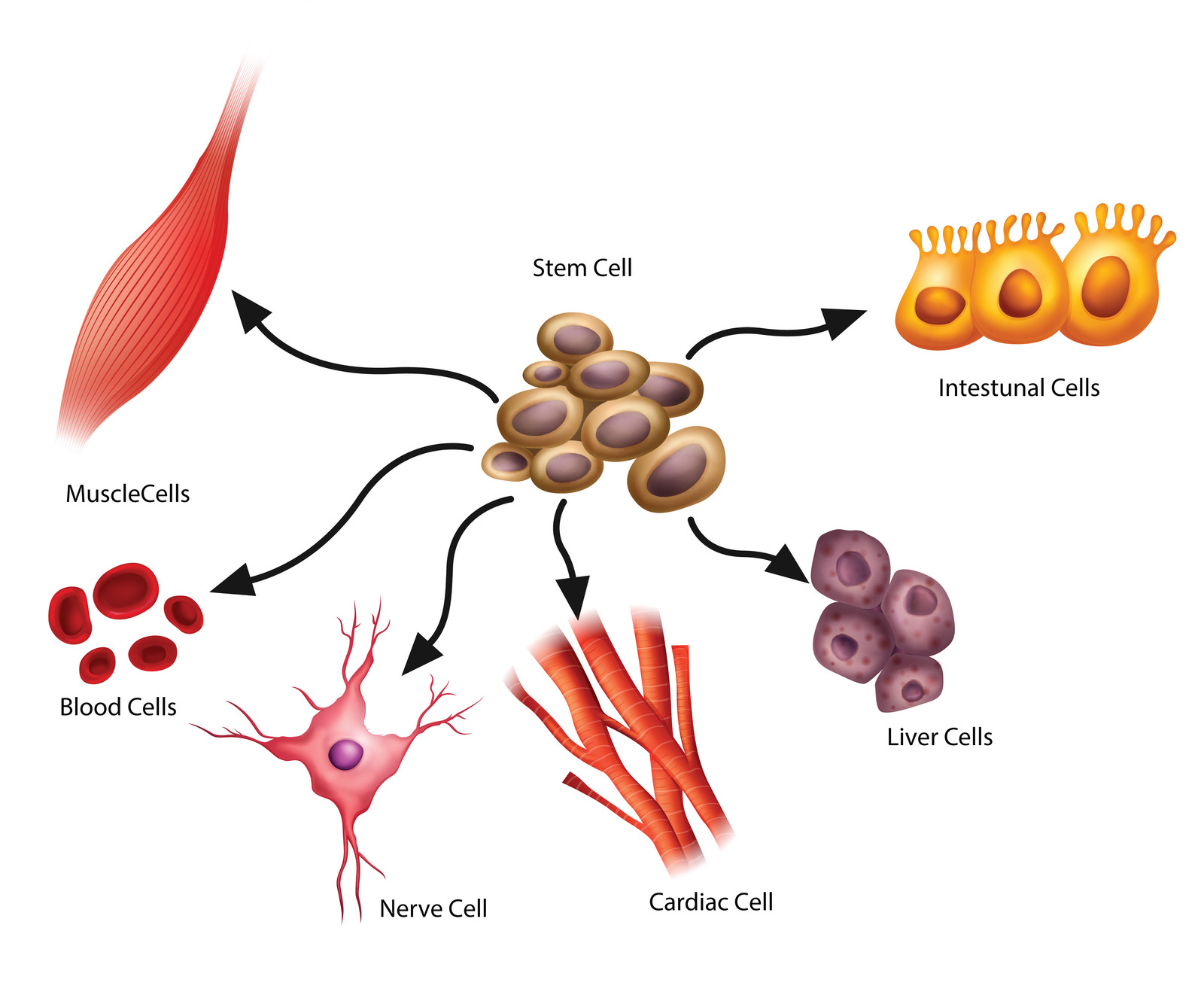
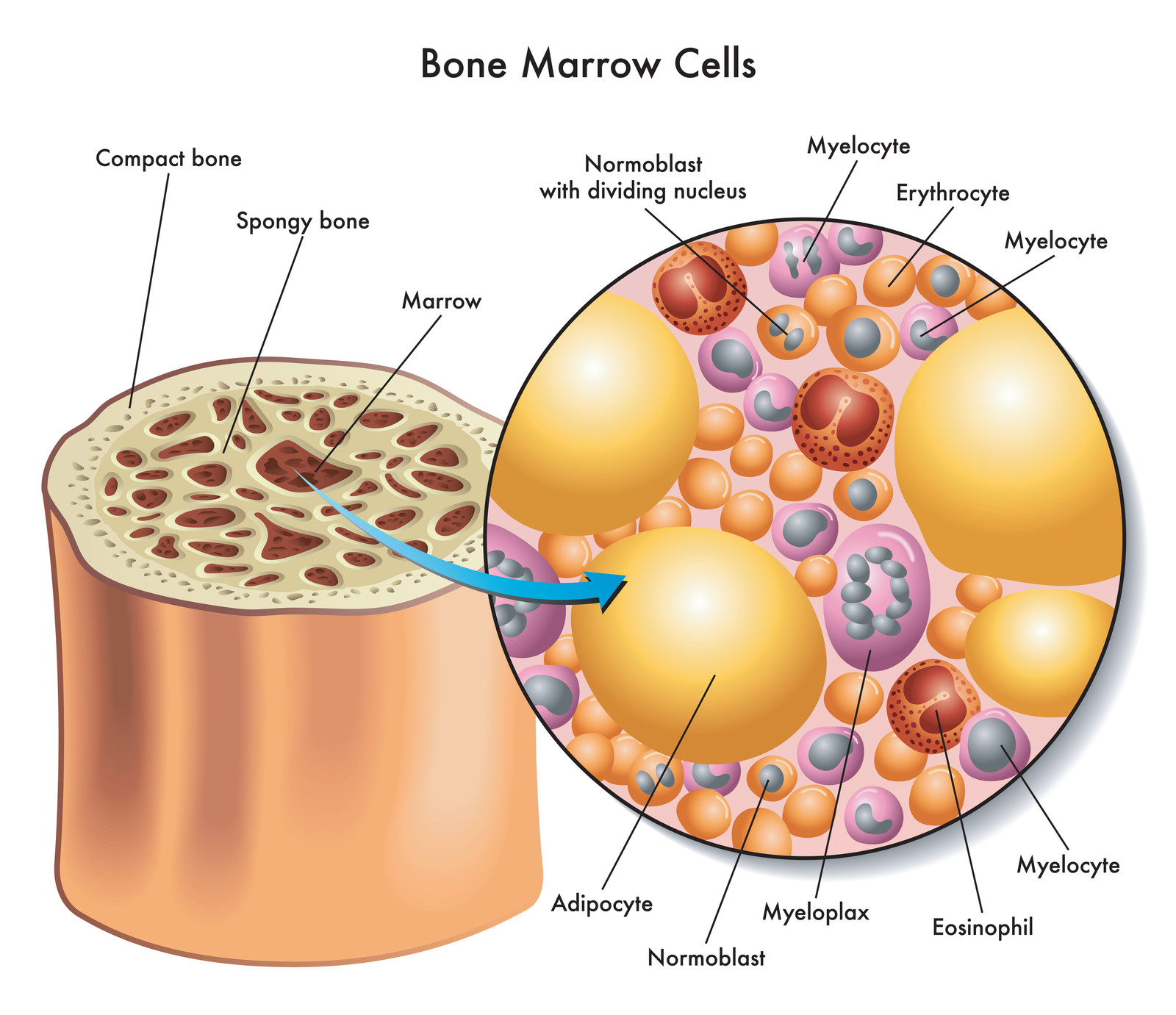
The hematopoietic stem cells
divide into blood cells.
Hematopoietic stem cells
Growth factors help stem cells
divide into various types
of cells.
Mesenchymal stem cells
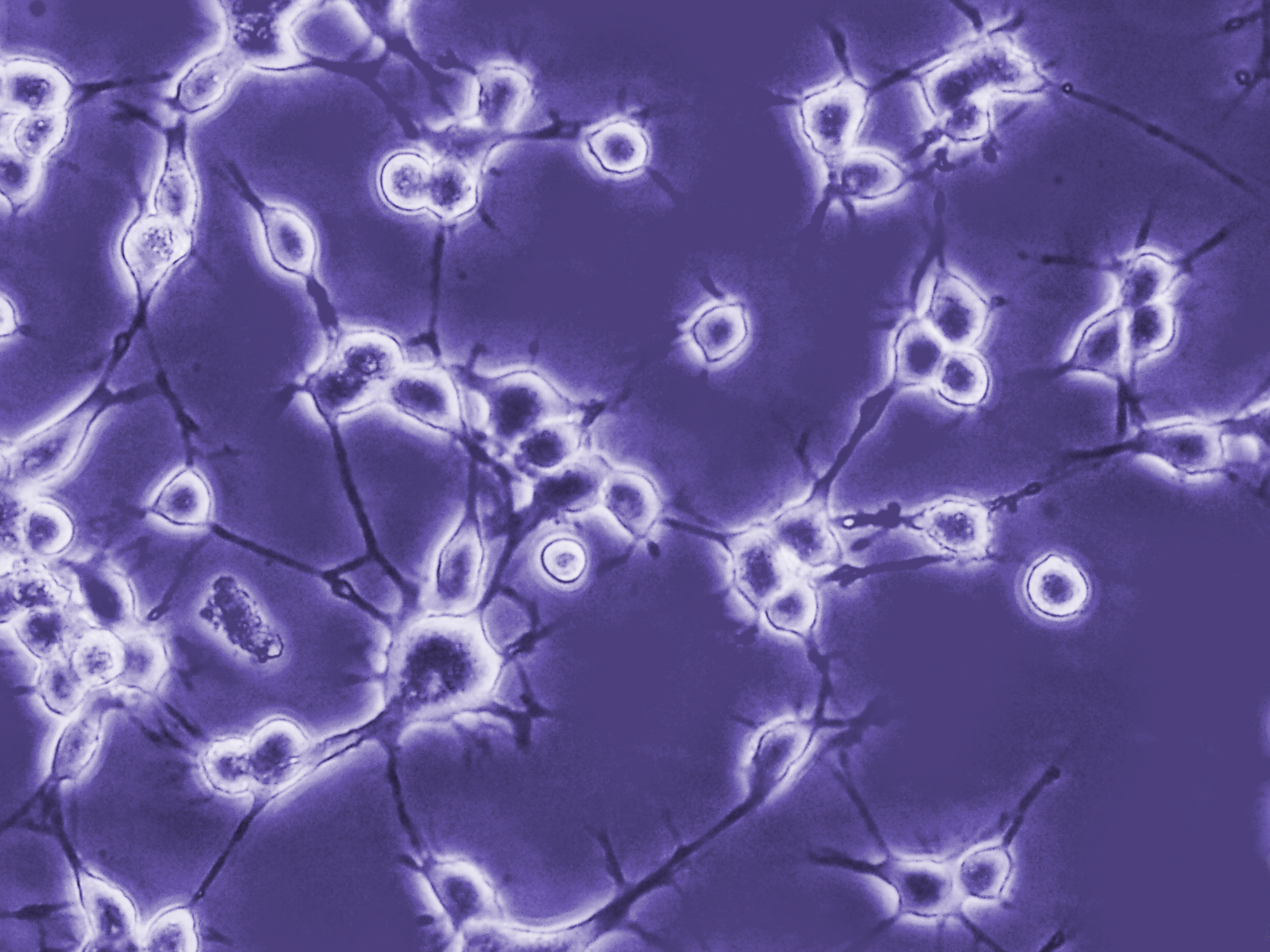
Neural stem cells divide
into neurons
Neural stem cells also
divide into astrocytes
and oligodendrocytes.
Your Major Stem Cells
Hematopoietic stem cells, mesenchymal stem cells and neural stem cells are your three major stem cells.
The hematopoietic and mesenchymal stem cells have their home or "niche" in your bone marrow, with the a large amount of stem cells in the hips.
Your neural stem cells have their "niche" inside your brain in two locations. The first niche is in the hippocampus, the center for learning and memory. The second location is in the "subependymal zone" of the lateral ventricles. These niches have low levels of oxygen so the stem cells are in a "quiescent" state, of minimal function.
This quiescent state allows the stem cells to survive longer, often as long as you live but they can also be mobilized to help repair or replace damaged brain cells. The niches are safe havens for stem cell quiescence and growth. They are also close to blood vessels that provide the area with oxygen, nutrients, and growth factors. The blood vessels also provide a pathway where the stem cells can circulate through the system to find and help injured cells.
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) were named for their production of blood cells or "heme." These stem cells produce your red blood cells, your white blood cells and other immune cells, including natural killer cells, neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, platelets, dendritic cells, lymphocytes and monocytes that can transform to macrophages. Hematopoietic stem cells also support injured cells with their growth factors that help the cells survive and repair the damage.
Hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow niche are mobilized into action when there is an illness or injury. They are also mobilized each day (in a circadian 24 hour cycle) to flow through the blood vessels, looking for cell damage. If there is bleeding, the hematopoietic stem cells signal to the bone marrow for a rapid expansion of progenitor cells to replace the injured cells, replace blood cells and send in immune cells to fight any infections.
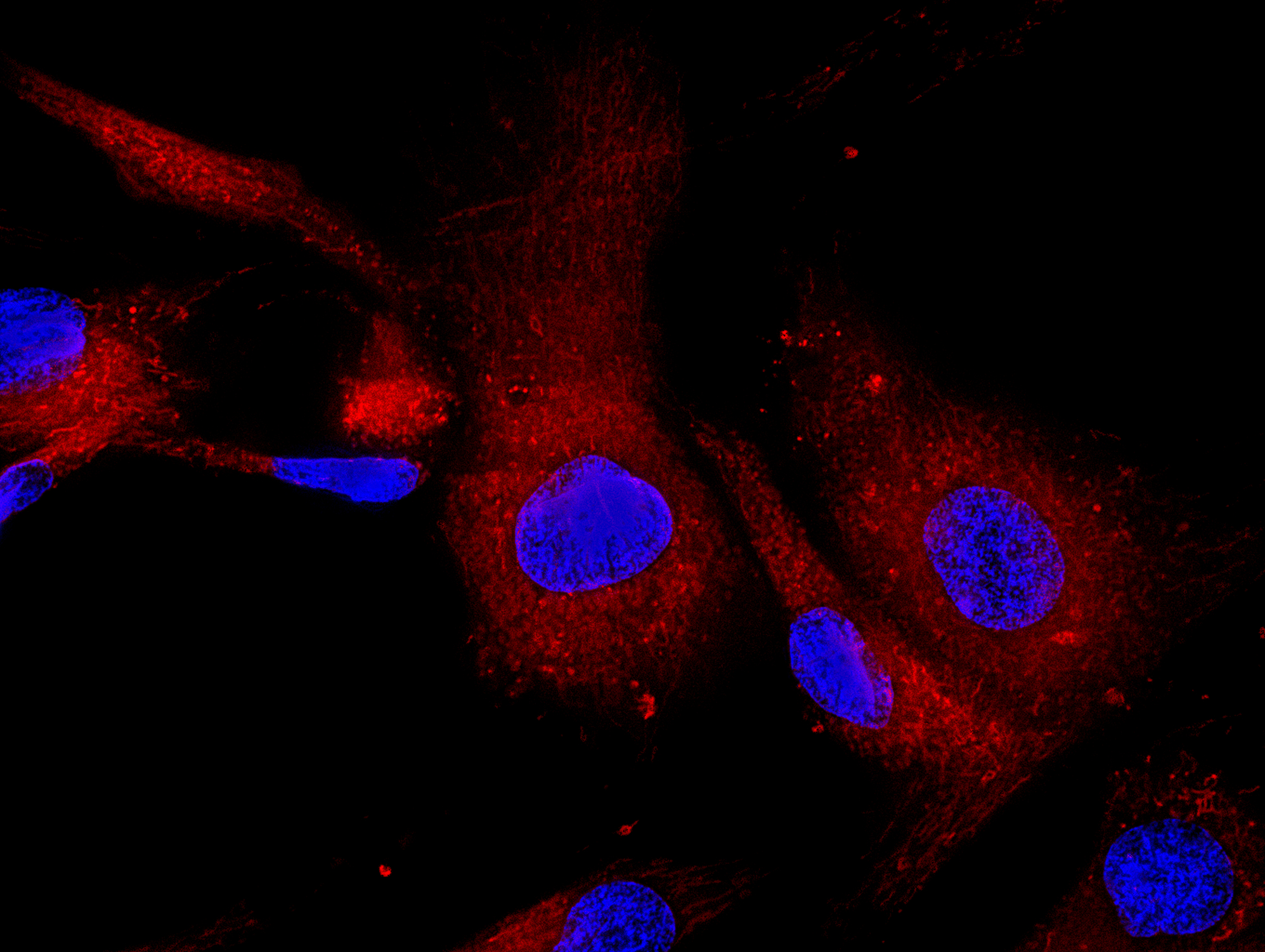
Mesenchymal stem cells reduce swelling (inflammation) and fight bad germs (viruses, bad bacteria, and fungus) in the body. They also divide into new cells that include bone cells (osteocytes), fat cells (adipocytes), cartilage cells (condrocytes) neurons and liver cells. Mesenchymal stem cells also support injured cells with growth factors.
Mesenchymal stem cells can divide into bone or cartilage or liver cells, etc. or they can divide into fat cells. The more sugar and fat foods that we eat, the more these stem cells have to divide into fat cells. There is an association between excess fat cells in the body and bone loss. If there is not enough strong bone to protect the stem cells in the bone marrow niche, it also reduces the blood cells and immune cells that the hematopoietic stem cells produce. There is therefore an association between bone strength and the production of blood and immune cells.
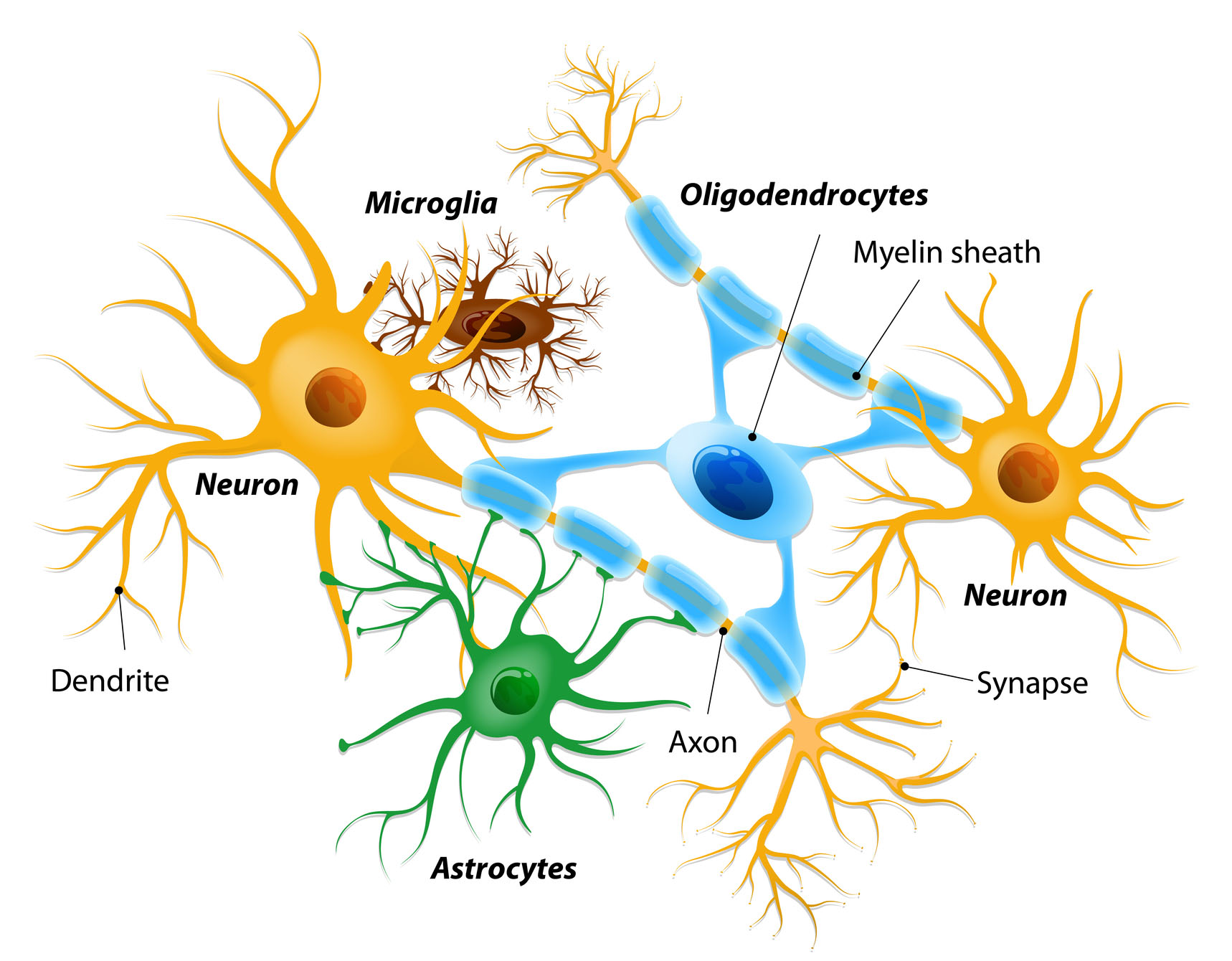
Neural stem cells divide into various brain cells that include neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes. Neurons transmit electrical signals to other neurons. Sensory neurons respond to stimuli such as touch, sound and light and motor neurons stimuli muscle contraction. Astrocytes are cells named for their star-like appearance (astro is Greek for star). Astrocytes support cells of the blood-brain barrier, that is a divide where large molecules and toxins cannot enter the brain. Astrocytes also provide protection and nutrition to neurons. They also repair damage in the brain and spinal cord by creating scar tissue to take the place of dead cells. In addition, astrocytes secrete a protein that produces myelin in oligodendrocytes. Oligodendocytes produce a myelin sheath that surrounds and insulates a nerve so electrical signals can move faster through the brain and spinal cord.
For more about the healing aspects of these and other stem cells,
click on Therapy for additional stem cell research.
Photographers/Graphic Artists
Bonemarrow - csp 20111460
© Can Stock Photo Inc./rob3000
Hippocampus - ID 47585822
© Decade3d/Dreamstime.com
Blood cells - csp 12252135
© Can Stock Photo Inc./Alexmit
Differentiation - csp 17796769
© Can Stock Photo Inc./Bluering
Mesenchymal stem cells - ID 36563629
© Volha Vshyukova/Dreamstime.com
Neurons - ID 32162718
© Dlumen/Dreamstime.com
Astrocytes - ID 47546395
© Designua/Dreamstime.com